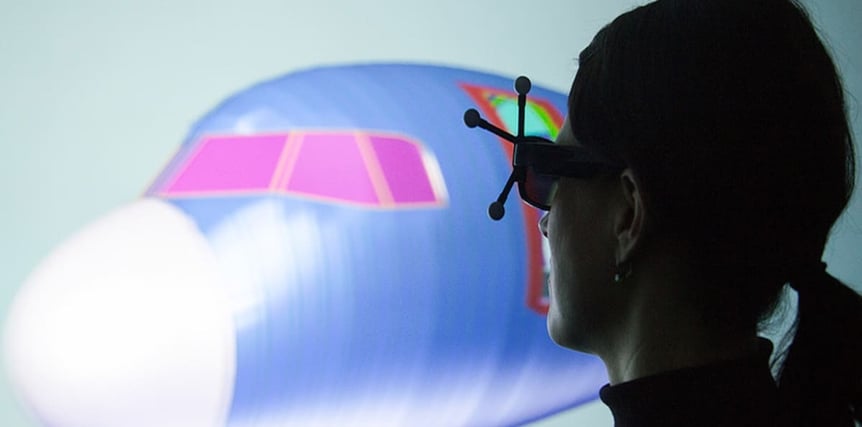
Designing and manufacturing aircrafts is quite a challenge. The million parts composing a plane must be as light as possible, while extremely resistant, and they must be assembled in a precise order. This has to be done in a context of fully globalized supply chains, with subassemblies prepared in different locations across the globe.
Hence you should watch for some key issues:
- The risk of conception errors is multiplied by the number of contractors and workers involved in the project
- The assembling process is very precise and requires optimized manufacturing plants and ergonomic workstations to operate efficiently
- Tests in real environment are not easy to carry out
- Many companies must collaborate with one another to design each individual part and conceive the final large-scale product
One solution to all these problematics is the use of Virtual Reality. A VR collaboration platform enhances the communication between engineers, by allowing them to work on a shared 3D model at scale 1:1 and in real time. In this article, we will explain how to optimize time-to-market and manufacturing operations thanks to virtual reality technologies.
Understanding modern aerospace engineering processes
What you need to build an aircraft or a spacecraft
Bulding an aircraft or a spacecraft relies on different materials, processes, and thus skills. For instance, you will need contractors that can work metal, others that can incorporate electric and electronics, others that can create ergonomic instrument panels… All these processes have been refined from ones used in the automotive industry, the computer industry, robotics, and many others. But this is only for the outside structure. With the advances in computer engineering and electronics, many new features are now included in subsystems and auxiliary equipment, and in the case of the defense industry, weapon manufacturing.
To create a full aircraft, a lot of work is needed in logistics, and preparing the assembling process. So, if you want to manufacture such large-scale products fast, while keeping the same quality, many optimizations should be done before the product hits production, and preferably without the use of a physical prototype. A faster prototyping process, such as reviewing your prototype in VR, speeds up time-to-market, especially if the different parts can be tested beforehand. Hence reducing the development time and any time spend replacing non-functional components.
You will also need a way to check for design errors. With the high requirements in the aircraft industry - and in the defense industry, as well as the number of contractors implied in this large-scale product manufacturing, there is a risk of multiplying errors.
How assembling an aircraft works
In the aerospace industry, you will have a prime contractor or a system integrator dividing the entire project between several subassemblies. For example, the rear fuselage section of a transport aircraft will be assembled separately from the rest of the aircraft, while the other sections are built in parallel. Then this part can also be divided between different subcontractors, who will in turn deal with their own suppliers for their own parts and modules. Then the different parts will be assembled, each sub-section first, then all subsections together (fuselage, wing tail, engine…) at the main assembly line.
The performance of each sub-section is verified prior to their assembly, to prevent mistakes. Tests are mainly done in simulated flight environment, incorporating different data such as wind, vacuum, temperature, or vibrations. The visualization of these abstract data can get a lot easier with the use of a virtual environment that can render each part separately, ensure that the virtual assembly happens correctly and that each part fits the technical requirements.
The final assembly is the most crucial step, for the company needs complex machinery that can fit and move large portions of vehicles. As the fuselage is assembled, it also moves through different workstations that will handle the auxiliary equipment, as well as the interior plumbing and electrical cables.
Once they are assembled, comes another round of verification. Even though some of the testing can be done beforehand with the virtual prototype of the aircraft, most of it will require the final product. However, the 3D model will be very useful at this step : it can be used as a basis to find errors in the assembly, or serve as a digital twin and replicate the ulterior changes happening in the final product.
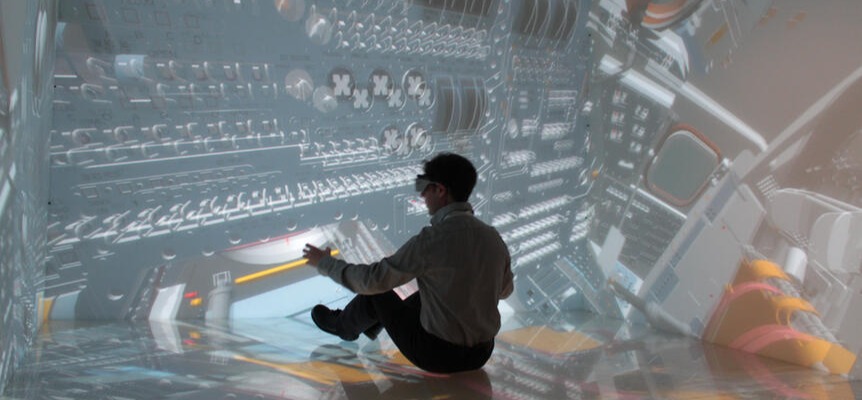

Using Virtual Reality to optimize aeronautics processes
Why the aerospace and the defense industry rely on virtual reality technology
Virtual Reality (VR) is the use of a computer modeling and simulation to enable a user wearing a vr headset (or glasses) to interact with 3D models and virtual objects in an artificial environment, and feel as if it was real. VR applications fully immerse the users in a virtual world that can resemble the real world or not. Huge developments of VR technologies were attained thanks to the projects funded by NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration). Virtual reality and the aerospace industry have strong ties.
Traditionally, the design of a new flight vehicle requires several design iterations. As not all design mistakes can be anticipated, substantial design rework can be common. 70% to 80% of aerospace product cost is determined at the design stage according to the Britannica Encyclopaedia. Therefore, the first thing manufacturers in the aerospace and defense industry should focus on optimizing their design processes, to better their overall time-to-market.
How virtual reality accelerates design and manufacturing processes
As we explained earlier, assembling a large-scale product such as an aircraft, requires the collaboration of many subcontractors. Manufacturing an aircraft is a long and complex process, as every manufacturer depends on several suppliers to build their own components. Not only does it bring remote collaboration issues, but also the more people are involved in the projet, the more errors can be made.
All these pain points can be simplified using a VR remote collaboration platform where every manufacturer can “plug” their CAD model and assemble them with the 3D data of the other companies. With a versatile VR software thought for engineers, the different contractors can work together in the same virtual environment, even if they don’t use the same CAD software to create their part (even though it is recommended that all contractors rely on the same 3D visualization software), or even if they are not located on the same site (or country).

Once in the virtual environment, each contractor can achieve the overall model with their own creation. They can collaborate over the internet without issues, and each assembler responsible for a large part of the project can easily review the model and look for design errors.
Other aspects of aeronautics where VR can help
Virtual Reality is a broad tool that can be very useful in other aspects of the aerospace and defense industry, such as the training of specialized collaborators, and helping technicians when they maintain the aircraft. Augmented and virtual technologies have been used in many fields to help businesses find smart solutions from design to market.
Want to know more about professional VR and how to use it? Check-out our other articles about XR, and how it could benefit your business:





 Back to Blog
Back to Blog