Many opportunities and challenges were brought by Industry 4.0 to the manufacturing industry. The new technologies connect digital and physical assets, which changes all the business processes. To embrace this radical change, companies must understand and master all the steps from product conception to selling. However, only Digital Champions have adopted these technologies today, and others will likely struggle to keep competitive. So far, only a few companies have emerged as Digital Champions and gotten all the benefits from Industry 4.0.
Here are the 8 digital transformation technologies you should adopt, to embark your company on your digital transformation:
- Integrated end-to-end supply chain planning
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Predictive maintenance of assets and products
- Manufacturing execution systems
- Digital twin of products and manufacturing line
- Collaborative robots, smart robots, robotic process automation (RPA)
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Virtual reality/augmented reality solutions
On average, Digital Champions have implemented nearly 2/3 of the most critical technologies that helped with their digitization, such as Virtual Reality. Want to see how VR display software can help you with your digital transformation, and optimize your business process from design to market?
1. Integrated end-to-end supply chain planning
Supply chain integration maturity is a key digital transformation technology. When your business model demands product customization and immediate shipment to the consumers, you usually rely on a strong supply chain with transparent and flexible processes. It is getting even more important, as your industry grows, and builds new warehouses and manufactures. You also have to take into account the data from other department such as production, R&D, inventory control, marketing…
An integrated E2E supply and demand planning provides a seamless transition between suppliers, logistics providers, manufacturers, and customers:
- All stakeholders have a complete and transparent view of the supply chain
- They see data simultaneously and can share it
- Partners can collaborate more extensively and develop synergies
- Demand changes can get an answer and prompt action throughout the supply chain in little time

2. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) aims to link the physical world to the digital world, enabling people and “smart objects” to be connected anytime, anywhere, using (ideally) any network and service. More specifically, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), along with the automation of the industrial manufacturing, is a significant technology that boosted the digital transformation of early adopters and initiated the Industry 4.0. IIoT services and applications provides solutions for:
- More effective scheduling, planning and monitoring of manufacturing operations
- Decentralized analytics and decision-making, with real-time responses
- Optimized productivity, efficiency, and maintainability of machines with available data
3. Predictive maintenance of assets and products
Predictive maintenance is a technique relying on monitoring tools that will track the performance of equipment and detect if there may be a defect. The objective is to fix these assets before they break. A key-element in this technique is the Internet of things (IoT), because they will rely on maintenance sensors to capture information, identify the important data and identify what part of the factory needs attention.
When a company relies on predictive maintenance, they will only require to maintain their equipment when it is necessary, thus saving lots of resources:
- The equipment is in maintenance for a shorter time
- The loss of production hours to maintenance is minimized
- The cost of buying spare parts and supplies is reduced
4. Manufacturing execution systems
In the 2000’s, many manufacturers invested in Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that enabled to plan and optimize the supply chain. The manufacturing execution system (MES) is the missing link between the data stored in the ERP and the operations in the workshop. A MES helps to raise the manufacture’s efficiency by connecting and monitoring the machines and work centers on the factory floor. By surveying all the data coming from your equipment, you can make sure you reach your production goals successfully and find areas of improvements for the manufacturing line. MES focuses on supervising workers and machines and keep records of them (traceability system).
5. Digital twin of products and manufacturing line
.jpeg?width=863&height=384&name=IMG_1733-1-1%20(1).jpeg)
Digital twins are virtual versions of physical assets (equipment or factories), or products, that can be used for digitally supported planning, scheduling or designing products. It is the most important digital transformation technology brought with Industry 4.0. Digital twins rely on AR/VR technologies to build a virtual model, that is an exact replica of the physical world, and the accuracy is maintained through real-time changes. It can be used at different levels in manufacturing:
- Check a critical component within the manufacturing process
- Monitor and improve a single machine, or the entire production line
- Surveying the overall design-to-market process
It enables companies to improve product quality, enhance traceability and reduce wastes. Digital twins work well with other digital transformation technologies such as predictive maintenance and VR simulations.
6. Collaborative robots, smart robots, Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotics designs, develops, and deploys robots. It can either be the sensor gathering data on the manufacturing line, or a robot created for a task or function formerly performed by humans. It is for instance the case for collaborative robots (or cobots), that are created to interact participate or eliminate dangerous or repetitive tasks in a workspace shared with workers. On the other hand, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is concerned with “how humans do things”, and attempts to mimic them, either in a hardware or software form.
When combined with other technologies, manufacturers can really take full advantage of robotics as a digital transformation technology. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and RPA are polar opposite, as one tries to replicate how human thinks, and the other how human does. See how they could benefit one another? With IoT, you can create a fully automated environment with RPA, because the different equipment will be able to communicate across platforms, devices, and manufacturers.
7. Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) has a lot of potential. Why using it in the manufacturing industry? Because if will boost the quality of your operational decision-making. AI will transform manufacturing in many ways, for example by enabling:
- Fully automated quality checks
- Prediction of failure modes
- Predictive maintenance using machine learning
- Generative design
For now, the core use-case are still emerging, because there are uncertainties about the maturity of the data produced by the AI systems themselves.
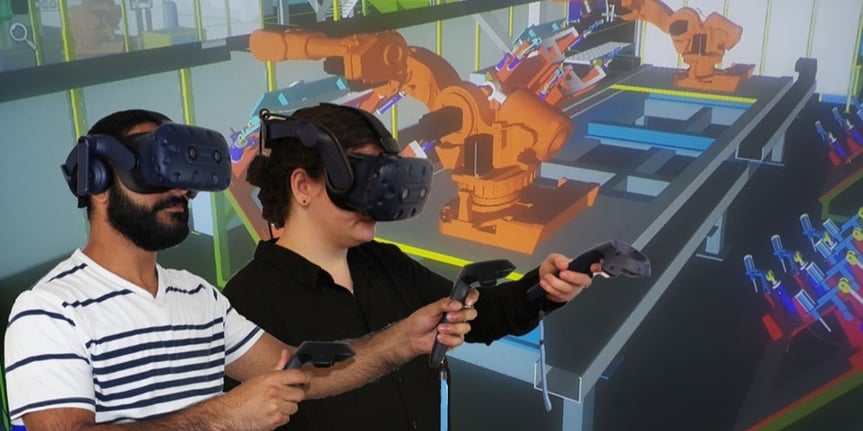
8. Virtual reality/augmented reality solutions
Adopting AR/VR tools in your industrial process is a sign of digital maturity. They help to visualize your product and/or your manufacturing process in a safe virtual environment. In a competitive business world where every downtime can lead to a revenue loss, and every product has to be tailored to the customer’s needs. See how reality technologies can help with your manufacturing?
With a VR display software like TechViz, there are several use cases with Virtual reality that can benefit your business, such as:
- Reviewing the design of a product, even complex or large-scale ones, with collaboration in VR
- Training your workers to be ready for operation and productive in the shortest time possible
- Simulating manufacturing process with VR simulation and 3D point clouds
- Optimizing the workspace ergonomics with body tracking





 Back to Blog
Back to Blog